Level shifter circuit schematics a conventional cross Circuit Diagram So R1 and R2 form a voltage divider, and R2 should be twice R1 to get the 0 V. Next we have to find the amplification, which is determined by R3 and R4: (the "to_adc" is the output voltage): The above non-inverting circuit is a bit like your summing amplifier. (e.g. > 5k) you will need to buffer the signal before sending to the level The simplest and most common method of logic level shifting is a voltage divider. In the circuit shown as in the first picture, the output of the divider is the line coming out from the middle. There is a total of 5V dropped across the circuit, but we can can calculate how much voltage is dropped across each resistor.

A level shifter circuit is used to convert signals from one voltage level to another while maintaining the shape of the signal. This is commonly needed when interfacing different parts of a system that operate at different voltage levels, such as between microcontrollers, sensors, or other integrated circuits.

A Comprehensive Study on the Design Methodology of Level Shifter Circuits Circuit Diagram
Bank1 can use an I/O voltage of 3.3 V or 1.5 V. Bank2 can use an I/O voltage of 2.5 V or 1.5 V. Top-Level Block Diagram The logic in this design example is the straightforward passing of data from inputs on one voltage bank to outputs on another voltage bank (Figure 2). The design does not consume any other logic than the routing resources and
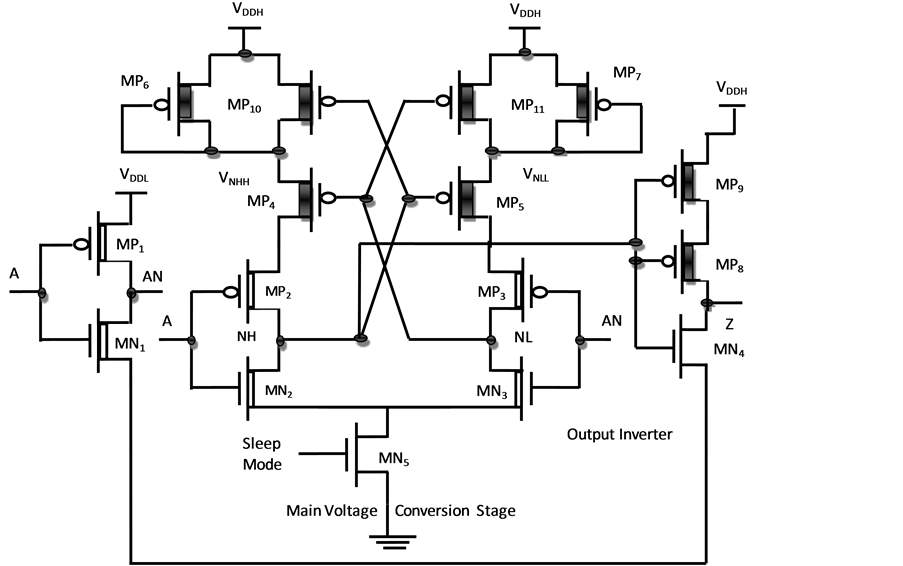
voltage signals themselves, requiring a level-shifter and hence high voltage switch control on their own. This is accomplished with two cross-coupled circuits like those shown in Fig. 4 where each cell provides the high voltage switch signals of the other. B. Complete level-shifter circuit From the timing diagram in Fig. 4 it is evident that the

Level Shifter Circuits: Theory, Design & Working principle Circuit Diagram
The level shifter (LS) circuit has become an indispensable circuit component in both analog and digital systems. In the past decades, there has been an exponential increase in the academic publications for the LS circuits to improve their performances and their applications. Therefore, this review paper provides a comprehensive study of the LS circuit, ranging from circuit topologies and